OpenAI
Introduction¶
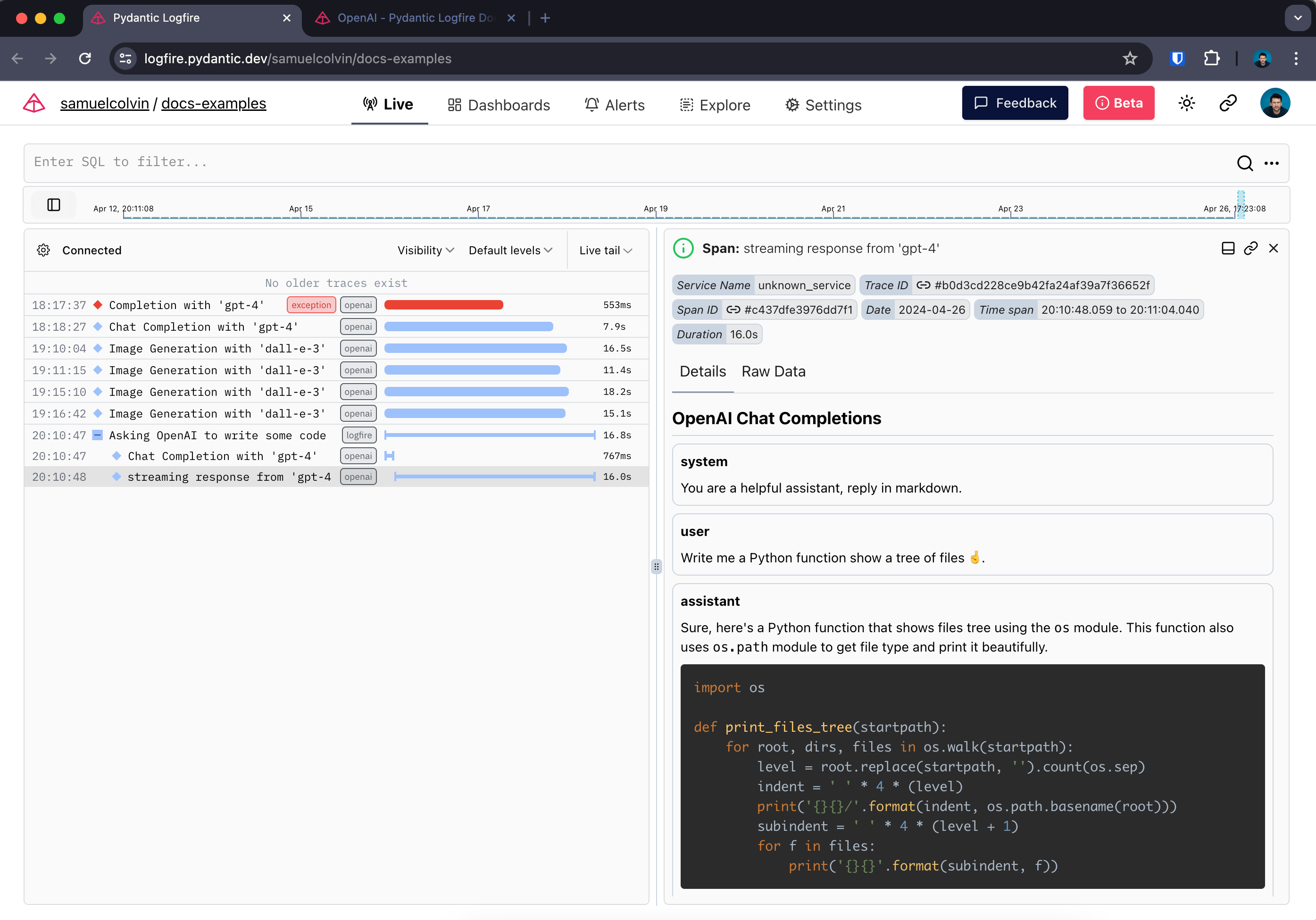
Logfire supports instrumenting calls to OpenAI with one extra line of code.
import openai
import logfire
client = openai.Client()
logfire.configure()
logfire.instrument_openai(client) # (1)!
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model='gpt-4',
messages=[
{'role': 'system', 'content': 'You are a helpful assistant.'},
{'role': 'user', 'content': 'Please write me a limerick about Python logging.'},
],
)
print(response.choices[0].message)
- If you don't have access to the client instance, you can pass a class (e.g.
logfire.instrument_openai(openai.Client)), or just pass no arguments (i.e.logfire.instrument_openai()) to instrument both theopenai.Clientandopenai.AsyncClientclasses.
For more information, see the instrument_openai() API reference.
With that you get:
- a span around the call to OpenAI which records duration and captures any exceptions that might occur
- Human-readable display of the conversation with the agent
- details of the response, including the number of tokens used

Methods covered¶
The following OpenAI methods are covered:
client.chat.completions.create— with and withoutstream=Trueclient.completions.create— with and withoutstream=Trueclient.embeddings.createclient.images.generate
All methods are covered with both openai.Client and openai.AsyncClient.
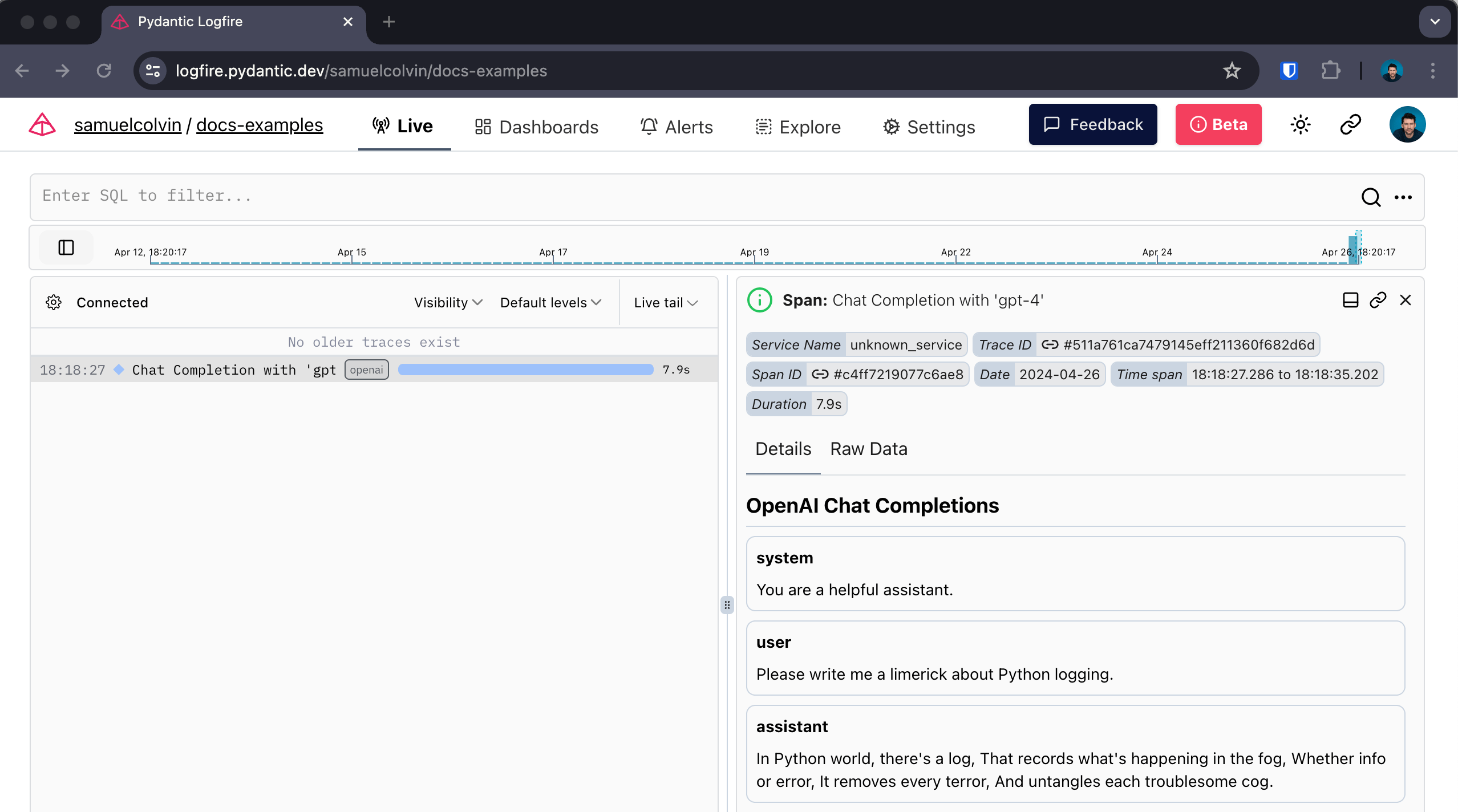
For example, here's instrumentation of an image generation call:
import openai
import logfire
async def main():
client = openai.AsyncClient()
logfire.configure()
logfire.instrument_openai(client)
response = await client.images.generate(
prompt='Image of R2D2 running through a desert in the style of cyberpunk.',
model='dall-e-3',
)
url = response.data[0].url
import webbrowser
webbrowser.open(url)
if __name__ == '__main__':
import asyncio
asyncio.run(main())
Gives:
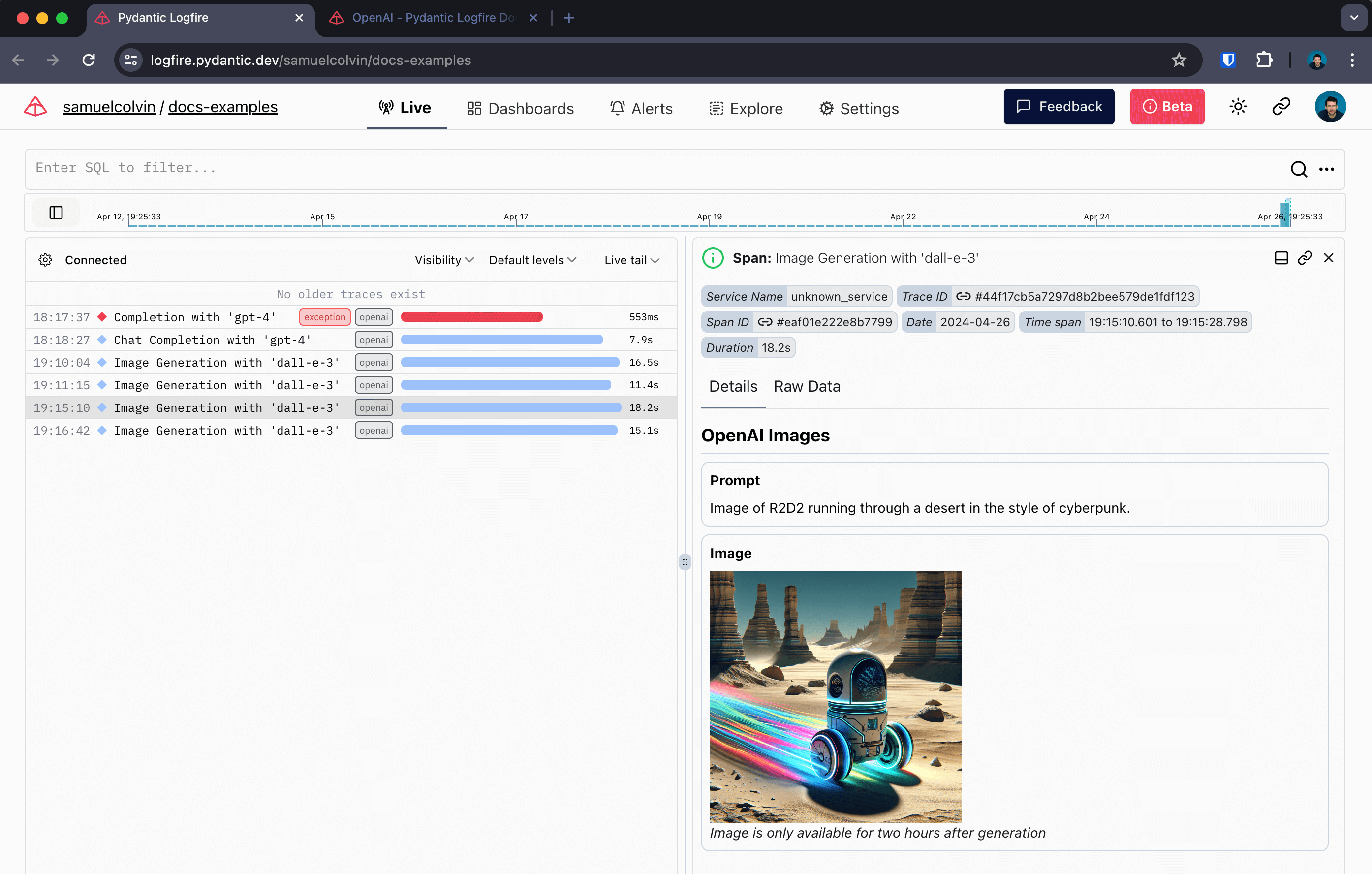
Streaming Responses¶
When instrumenting streaming responses, Logfire creates two spans — one around the initial request and one around the streamed response.
Here we also use Rich's Live and Markdown types to render the response in the terminal in real-time.
import openai
import logfire
from rich.console import Console
from rich.live import Live
from rich.markdown import Markdown
client = openai.AsyncClient()
logfire.configure()
logfire.instrument_openai(client)
async def main():
console = Console()
with logfire.span('Asking OpenAI to write some code'):
response = await client.chat.completions.create(
model='gpt-4',
messages=[
{'role': 'system', 'content': 'Reply in markdown one.'},
{'role': 'user', 'content': 'Write Python to show a tree of files 🤞.'},
],
stream=True
)
content = ''
with Live('', refresh_per_second=15, console=console) as live:
async for chunk in response:
if chunk.choices[0].delta.content is not None:
content += chunk.choices[0].delta.content
live.update(Markdown(content))
if __name__ == '__main__':
import asyncio
asyncio.run(main())
Shows up like this in Logfire: